The Institute of National Colleges of Technology, Japan (The Institute)
establishes and operates KOSEN, National collages of technology, in all
over the nation. In its operational goals and objectives (duration: from
April 1, 2009 to March 31, 2014), the Institute describes its policy in
relation with securing outstanding faculty as "to employ people having
excellent capability as educators such as those who produced satisfactory
results in private companies". It also describes its concept that
the Institute helps to strengthen the collaborative framework with industries
etc.
As part of this, an extracurricular lesson "VR (virtual reality) Course"
started in October 2010 at Fukui National College of Technology (Fukui
Kosen).
his issue picks up Fukui Kosen. We focus in particular on the "Advanced
Research Center for Regional Cooperation" established to promote joint
research and academic exchanges between the college and the local community,
"Department of Civil Engineering" that has focused on diversified
and emergent possibilities brought about by VR technologies and used VR
tools in classes, as well as "Spatial Information Engineering Lab.",
led by Associate Professor Kazuhiko Tsujino of the school.
We also interviewed the 5th graders of Dept. of Civil Engineering who are
actually taking the "VR Lesson".
 |
|
 |
 Associate Professor Kazuhiko Tsujino, Associate Professor Kazuhiko Tsujino,
Dept. of Civil Engineering |
|
 Associate Professor Tsujino Associate Professor Tsujino
and 5th graders of Dept. of Civil Engineering,
with Special Associate Professor Kannonji
(FORUM8, right in the back row) |
| More Than 1,000 Students Gather at the Foothold for Nurturing Research
and Development Engineers |
Fukui National College of Technology (Fukui Kosen) is a national, advanced
educational institution that provides junior high school graduates with
five continuous years of technical education and nurture them into research
and development engineers. Fukui Kosen was founded in 1965. Under partial
amendment of the National School Inauguration Law, it was originally established
with temporary school buildings in Takefu city, Fukui Pref., providing
three courses: mechanical engineering, electrical engineering, and industrial
chemistry courses.
In the next year of 1966, the School moved into newly constructed school
buildings in Geshicho, Sabae as it is known today. The old building was
closed. Civil Engineering Course was established in 1970, and Department
of Electronics and Information Engineering in 1988. In 1993, Department
of Civil Engineering was reorganized into Department of (Environmental
Urban) Civil Engineering. In 1995, Department of Industrial Chemistry was
reorganized into Department of Chemistry and Biology Engineering. In 1998,
the Advanced Engineering Course was established with Production System
Engineering and Environment System Engineering.
Under the Act on the Institute of National Colleges of Technology, Independent
Administrative Agency (promulgated and put into effect in 2003), Fukui
Kosen was established and started operation under the Institute since April
2004 with other national colleges of technology.
In 2005, Department of the Electrical Engineering was reorganized into
Department of the Electrical and Electronic Engineering. In the same year,
the Japan Accreditation Board accredited the educational program of Production
System Engineering of the Advanced Course of Fukui Kosen for Engineering
Education, JABEE, in the field for General and Combined Engineering for
the first time among the universities in the Fukui Pref.
Through these transitions, Fukui Kosen has 5 main departments including
Departments of Mechanical Engineering, Electrical and Electronic Engineering,
Electronics and Information Engineering, Chemistry and Biology Engineering,
and Civil Engineering. Above these educational courses of Kosen over 5
years (Associate degree course) is specialized, 2-year Advanced Engineering
Course (bachelor's degree courses) consisting of Production System Engineering
Course and Environmental System Engineering Course.
The quota of a class in each department is 40, and the total number one
grade is 200 for all five departments. The quota of the Advanced Course
is 20 (12 for Production system Engineering and 8 for Environmental System
Engineering). In addition to the school buildings, indoor / outdoor athletic
fields and library, the campus of about 100,000m2 also has a dormitory.
As of May 2010, 1,011 students in total of 1st to 5th graders in the main
courses and 57 students in total of 1st and 2nd graders in the Advanced
Course are on the register roll.
 |
 More than 1,000 students are learning in the campus of about 100,000m2 More than 1,000 students are learning in the campus of about 100,000m2 |
In 1991, Fukui Kosen Hi-Tech Education and Research Center was established
not only to enhance the education and research system in the school but
also to promote joint research and technical consultation with regional
companies. In 2004, the Regional Cooperative Laboratory for traditional
industry was established. After the Hi-Tech Education and Research Center
was reorganized into the Advanced Research Center for Regional Cooperation
in April 2005, it has been performing various action plans aiming at “regional-based
development of human resources and technical support”, for example, establishment
of Regional Cooperative Laboratory and Satellite Lab (a rental laboratory
space for companies).
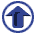
The Center reorganized its research areas in 2006 into 7 sections of “Regional
Alliance & Culture”, “Environment & Biology”, “Energy”, “Safety
& Disaster Prevention”, “Information & Telecommunications”,
“Material & Processing”, and “Measurement & Control” to make
it easier to understand and consult, making full preparations to receive
users. This helps to improve regional contribution. In addition, Entrepreneur
Support Center was established in the Center to support rearing entrepreneurs
and business creation.
 |
|
 |
 Advanced Research Center for Regional Cooperation (ARC) that performs joint
research with local companies and supports business creation Advanced Research Center for Regional Cooperation (ARC) that performs joint
research with local companies and supports business creation |
|
 7 research sections of the ARC 7 research sections of the ARC |
| High Ratio of Students Receiving Tentative Job Offers |
Department of Mechanical Engineering aims to cultivate students who have
synthetic ability as an engineer by learning mechanism of machinery and
practice product manufacturing, while Department of Electrical and Electronic
Engineering aims to cultivate creative engineers who have knowledge about
state-of-the-art technologies covering wide ranges of electricity and electronics.
Department of Electronics and Information Engineering aims to foster engineers
capable of solve problems by way of both software and hardware. Department
of Chemistry and Biology Engineering aims to educate students who learn
material engineering and biological engineering in a chemical point of
view and are able to make the best use of chemistry. In contrast, Department
of Civil Engineering aims to educate engineers who create environmental
cities, infrastructure, and architecture for residents in order to realize
a sustainable recycling-oriented society.
“It is our strong point that every graduate can get a job without fail
unless he or she sticks to a particular one.” Says Associate Professor
Kazuhiko Tsujino, referring to one of the advantages of learning at Fukui
Kosen, adding that this might also be true about other Kosen, national
technical colleges.
For example, though the situation around civil engineering is particularly
severe, the graduates of Dept. of Civil Engineering of the school in March
2011 got more than 200 job offers from in and outside the Pref. Since about
half of the students of the Dept. get jobs in public agencies and the other
half continue studying after leaving school, the job offer rate for one
student exceeds 10. One of the five departments had the offer rate of over
20. According to the school, the ratio of students of the main courses
receiving tentative job offers is 100%.
When a student enters a higher-level school, he or she enrolls into the
3rd grade of a university or enters the advanced course of Kosen. When
completing the advanced course, the student can get a bachelor’s degree
from National Institution for Academic Degrees and University Evaluation,
and also enter into a graduate school.
Regarding the two courses that compose the Advanced Engineering Course,
Production System Engineering Course is based on the three Departments
of Mechanical Engineering, Electrical and Electronic Engineering, and Electronics
and Information Engineering; while Environment System Engineering Course
is based on Departments of Chemistry and Biology Engineering and Civil
Engineering.
| Dept. of Civil Engineering and Tsujino Lab. |
The Department of Civil Engineering not only provides major subjects in
the fields of structure, planning, and environment, but also builds up
unique education to develop creativity such as ‘Science for Design and
Manufacturing’ (1st grade) and 'Surveying Contest' (2nd grade), and 'Building
a City Using VR' (3rd grade). The Dept. also puts emphasis on external
activities such as participation in 'National Technical College Design
Competition' (e.g. Bridge Contest), 'Natural Environment School (Eco Lab)',
Class on Demand, joint projects with Society of Architects and Building
Engineers.
The Dept. is continuously evolving to meet the needs of the changing society.
When the former Dept. of Civil Engineering was reorganized into the present
Dept. of (Environmental Urban) Civil Engineering, curriculums in the fields
of environment and information were added to that of civil engineering
instructed so far. Since 2007 academic year, a curriculum in the field
of architecture has been expanded so that students can be qualified for
taking an examination of first-class registered architects.
"My major is sediment disasters. In my research, using satellite image
data and such, firstly the occurrence point of a sediment disaster is found.
Then dangerous places are narrowed down by analyzing the geological characteristics,
landforms, or vegetation."
Associate Professor Kazuhiko Tsujino is in charge of the subjects such
as surveying and applied surveying, spatial information engineering, design
and drawings for environmental urban engineering, experiments and training
for environmental urban engineering. Tsujino Lab is also making research
on disasters including sediment disasters as its core, using up-to-date
surveying tools and remote sensing data. Recently, a study commissioned
by the local municipality is ongoing to identify the behavioral pattern
of wild animals by putting GPS (Global Positioning System) collars and
apply them to precautions against wildlife damage.
| Introducing a Subject for Training UC-win/Road |
It was several years ago that Associate Professor Kazuhiko Tsujino first
experienced UC-win/Road, 3D real-time VR software of FORUM8. He says that
when he visited INTEX OSAKA with his students to take part in the Bridge
Contest, he was interested in it at the first sight of its demonstration
in our booth exhibited in the fair held at the same time.
"Partly because I was teaching CAD at school, I was interested in
VR technologies from the beginning."
Later, when it was asked to propose a project showing the attractiveness
of Department of Civil Engineering to the new students on the headmaster's
discretionary expenses, he applied for it with his own point of view that
he wanted to use UC-win/Road as a tool to help educate students who have
new knowledge of VR. In 2006, his proposal was adopted. Through preparation
period, the class using UC-win/Road started from "Experiments and
Training for Environmental Urban Engineering" in the first term of
2007.
The Experiments and Training class is one of the experience and training
subjects. "Experiments and Training for Environmental Urban Engineering
I" for the 2nd grade is a training class for surveying providing a
lecture followed by the students' activities in groups actually creating
maps in the school. In contrast, classes for the 3rd grade (II) and the
4th grade (III) provide various themes such as material experiments and
earthquake engineering at the same time. Each class is two hours and a
half long, held once a week. Students work on one theme for 2 weeks (five
hours in total) as a group, receiving practical training and submit reports,
then moving on to another theme in turn. Use of UC-win/Road was incorporated
as one of the themes. Though the subject covers the whole year, different
themes are set for the first and last terms respectively.
| Providing "VR Course" from the Last Term of 2010 |
With promotion of manufacturing products as its vision, Fukui Kosen provides
education of manufacturing products in all Departments of the main course
and the Advanced Engineering Course. In recent years, information network
technology (ICT) based on the Internet is becoming far more important,
and ICT is essential for product manufacturing technology. The Advanced
Research Center for Regional Cooperation of the School applied for projects
of "Program for Making the Best Use of Corporate Engineers and others"
by the Institute of National Colleges of Technology with a concept of practicing
emerging technologies such as ICT and VR in addition to the conventional
product manufacturing and basic technologies through joint education (title:
Development of joint education to fuse ICT and the local communities).
Then in March 2010, Associate Professor Kazuhiko Tsujino proposed to invite
a specialist from a private company as an approach to joint education of
companies and Kosen in the program, aiming also to learn VR techniques
himself. Ideally speaking, he wanted to have the instructor from the graduate
of Kosen, but thinking, "VR is a new technology and the specialist
in FORUM8 must be the right person because we had already used FORUM8's
UC-win/Road", he consulted with the head of the Advanced Research
Center for Regional Cooperation, and his plan was admitted.
When it was expected that the proposal would be adopted, he asked FORUM8
to select a suitable instructor. Nahomi Kannonji, VR Support Group of the
Osaka Branch was recommended. In September of the same year, she was assigned
to Special Associate Professor of the school.
In the last term of this year (October 2010 to February 2011), an extracurricular
class "VR Lesson" is held biweekly, two courses at a time, 10
times in total (table 1).
| Table 1. Overview of VR Lesson |
- Lecture and praqctice required for the data creation along the theme
- Basic knowledge of CG/VR
- CG model conversion, process of images, operation of VR application
- The acquisition of VR simulation data creation techniques based on each
theme and the presentation skills involving the created VR data.
| Schedule(Latter period of 2010) |
- 1st Process of coordinate and images and filtering + practice(Selection
of theme)
- 2nd 3D modeling + practice
- 3rd Rendering + practice
- 4th Animation + practice
- 5th Image information and extraction + practice
- 6th Image compression and input/output + practice
- 7th Perception and 3D movie + practice
- 8th CG system and specifications + practice
- 9th VR system + practice
- 10th Intellectual property rights and security + VR contest
|
 |
|
 |
 Extracurricular "VR Lesson" using UC-win/Road has been provided
since the last term of 2010 academic year. Extracurricular "VR Lesson" using UC-win/Road has been provided
since the last term of 2010 academic year. |
| Views of the Students Taking "VR Lesson" |
We interviewed 6 students, who are in the 5th grade of the Dept. of Civil
Engineering and have already decided the companies to join or schools to
continue studying. All of them had already experienced UC-win/Road in the
class "Experiments and Training for Environmental Urban Engineering
II" for the 3rd grade (in the first term of 2008). Basically, they
used UC-win/Road in "VR Lesson" in this term after two years
since then.
"Compared with the experiments and training when there was constraints
of time, the instructor teaches us from the basic to application by taking
enough time in this lesson", says Mr. Hiroto Kawasaki in the Sanitary
Engineering Lab and others, to list one out of several advantages of this
lesson.
Mr. Akihiko Sato (Urban and Architectural Design Lab) thinks that UC-win/Road
is an effective tool for presentation that is easy to understand visually.
To improve usability, he also expects that a function will be added to
go back to the previous status with easy operation.
"To tell the truth, this is the third time that I use UC-win/Road,"
says Mr. Naoki Emi (Spatial Information Engineering Lab). Since he realized
the fascinating aspects of VR through the experiments and training, he
created 3D models using Google SketchUp for his graduation research at
first. Then after the opening of this course, he touched UC-win/Road again
and knew the 3D models he had been creating could be incorporated into
UC-win/Road, deciding to integrate the data created with each tools.
Mr. Kenta Asakura, Mr. Shunya Domae, and Mr. Daisuke Kawaguchi were also
working on graduation research assignment on their own in the same Spatial
Information Engineering Lab. They cooperated with Mr. Emi's work, and Mr.
Kawaguchi talked about the significance of producing one VR work in collaboration.
Mr. Naoki Emi, who is going to work in the field of electricity, and Mr.
Shunya Domae, who is going to work in the field of waterworks, keep using
of VR for making simulation or presentation in mind for the engineering
works they will take charge of in the future.
Similarly, those who are going to enter into a higher-level school also
want to keep on exploring possibilities of using VR in relation with their
majors. Mr. Akihiko Sato and Mr. Daisuke Kawaguchi are going to construction
and architecture-related college, and Mr. Hiroto Kawasaki will enter into
the Advanced Engineering Course of Fukui Kosen, Environment System Engineering
course.
"My interest in creating a town made me choose this course,"
says Mr. Kenta Asakura, who is going to work in the field of printing.
Knowing the joy of creating a town in a virtual space again, he wants to
make such knowledge an asset for the future, though it seems to be irrelevant
to the field.
 |
|
 |
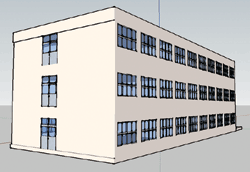
 In VR Lesson, models of the present situations and repair plans of the
vicinity and inside of Fukui Kosen. In VR Lesson, models of the present situations and repair plans of the
vicinity and inside of Fukui Kosen.
The 3D model created with Google SketchUp is read into UC-win/Road (right). |
| Towards the Next Academic Year |
Associate Professor Kazuhiko Tsujino considers applying for continuing
the project under the Advanced Research Center for Regional Cooperation
next year. With this in mind, he says, "Our goal is to be able to
take part in VR contest next year." In addition, in the Advanced Engineering
Course, he is willing to examine application of VR technology using UC-win/Road
in the subjects he teaches such as Information engineering for creativity.
(Interviewed & written by Takashi Ikeno) |