|
The National Institute of Technology (NIT), Japan (established in 2004) has established 51 national colleges of technology including National Institute of Technology, Oita College. At present, "KOSEN (Colleges of Technology) 4.0 initiative" is in operation (for 5 years from fiscal 2019) for the purpose of improving the characteristics of individual technical colleges with personnel development, local contribution and globalization as the core. At the same time, setting the two years before it as its preparation period, NIT supported the start-up cost for this activity. For this, the following projects of National Institute of Technology, Oita College were adopted as the supported projects of the Initiative: 1)"agri-engineering education" that aims at fostering engineers who have talent of agricultural sciences by cooperation between agriculture and engineering in fiscal 2018, and 2) "Disaster-resilient mind education" that aims at fostering engineering who have both basic knowledge about disaster prevention / reduction and resilient mind in fiscal 2019. Of the two activities, Associate Professor Mae is deeply involved with the latter one, too.
Furthermore, a material-related project they work on in cooperation with other plural technical colleges was adopted to NIT's subsidized projects open to the public from 2020 "advancement of social implementation education of emerging technologies (GEAR5.0)". It has started to move as a new educational research project.
|
|
 |
Tsunami attack simulation based on shallow water equations with the idea of software countermeasures of
disaster prevention |
|
Making full use of ICT, They Make Diverse Efforts in Structural Analysis, Designing Environment or Landscape
Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, to which Associate Professor Mae whom we interviewed belongs, is aiming at creating safe, comfortable, and convenient social infrastructure based on civil engineering knowledge. There, the following 3 items are set as main approaches; 1) "Structural system" to treat materials, structure, soil, and ground etc., 2) "Environmental system" to treat rivers, water supply and sewage, water resources, harbors, and coasts etc. , and 3) "Plan / architecture system" to treat cities, architecture, parks, and transportation etc. "I originally specialize in the architecture-related field, having structure (to be treated) in common with civil engineering," says Prof. Mae. More than 20 years ago when he was studying in Tokyo Denki University Graduate School, he took part in the design practice as a student assistant (SA). That practice class was held by connecting Tokyo and Kyoto Institute of Technology (Yamaguchi Laboratory) through a network. He remembers that he was conducting a method that would lead to today's remote work (working at home) before others.
 |
 |
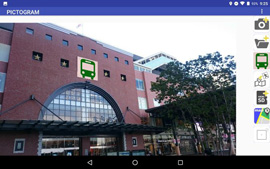
| Execution window after integrating images |
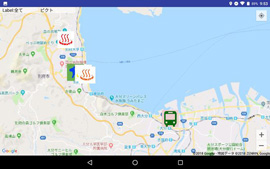
Map on which pictograms are displayed |
|
|
Partly due to this background, the subjects he takes charge of in the Department includes information processing, structural mechanics, city and environment design, and experimental practice. On the other hand, the Lab is working on a range of activities as follows; 1) Proposal of architecture to which forms and phenomena existing in the natural world are applied using algorithmic design, 2) Research and development of smartphone applications (apps) to use for diverse studies and lectures, 3) Studies on disaster prevention and environmental conservation using ICT, and 4) landscape simulation focusing on signs and colors.
|
Above all, the subject which is conspicuously studied in recent years is creating or studying smartphone apps in consideration of using them as the aid to their own studies or as the educational material.
For example, in the field work for examining a sign plan, a smartphone app for sharing information without stress among concerned people is created by pasting pictograms etc. on a photograph shot on the spot (image integration). These images are pasted on a map with location information. A function of route guidance to the spot is also added. Its outcome was reported in "ICRP 2019 (4th International Conference on Rebuilding Place)" held in Malaysia in November, 2019. They are also planning to extend it to tourism, examination of landscape as well as creation of hazard maps.
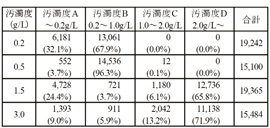
Besides, as a countermeasure to cope with environmental problems brought about by red soil erosion etc. in Okinawa pref., he and others developed a smartphone app capable of measuring the degree of pollution of suspension water containing red earth etc. accurately and easily. They obtained color information from the smartphone image of suspension water shot at the settling basin, and verified whether it is possible to estimate the degree of pollution. While comparing this with the results of other measuring methods, they are trying to improve the app for practical use including improvement in accuracy.
 |
 |
| Suspension water collected in the settling basin |
 |
|
Execution window of the app
(degrees of pollution: 3.0 g/L) |
Distribution of the degree of pollution of
respective suspension (image pixel) |
|
How to Introduce and Use UC-win/Road and Other FORUM8 Products
The first FORUM8 product for Associate Professor Mae to treat was Multiframe introduced in 2014. At that time, it became necessary to make frame structure analysis about structures of complicated and special forms as part of algorithmic design. Then the software, which he had already tried to use several times and found convenient, was formally adopted. Since then, he has been proposing structures of unique forms based on the analysis results it gave with validated strength.
On the other hand, his first direct contact with UC-win/Road came a few years later in 2018. As said above, it fell on the time when National Institute of Technology, Oita College was preparing for specifying disaster-resilient mind education to get adoption as the aided project for "KOSEN 4.0" Initiative.
"When trying to develop disaster-resilient mind as a school," there was a new need for making "simulation of debris flow in connection with disaster prevention and mitigation." Since debris flow simulation that would meet the need was provided as the plug-in of UC-win/Road, it was decided to introduce them as a set after examination among people concerned within the College. He also started to use them by himself in Feb., 2019. Since then, they have been used both in the studies in Mae Laboratory and classes of the College.
First, in the Lab in the fiscal year of 2019, with the students doing graduation research as its core, they learned how to operate UC-win/Road and the debris-flow-simulation plug-in. Utilizing them, the 5th graders of Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering made research into creation of a hazard map using debris-flow analysis simulation that focused on break and overflow of reservoirs.
At the same time, in the subject "experimental practice IV" for the 4th graders of the College, 6 uses of advanced ICT in relation to i-Construction were set as its theme. It describes information utilization through the following items; 1) 360 degrees camera, 2) Drone, 3) Laser range finder, 4) generation of point cloud data from photographic images, and 5) town planning Examination using UC-win/Road, which Associate Professor Mae takes charge of, and 6) debris-flow simulation.
 |
| Members of Mae Lab. |
In fiscal 2020, being restricted by the influence of new coronavirus since the beginning of the year, new 5th graders who prepare for graduation research have been learning both tools and experiencing simulation using them since the previous year. In addition, based on this knowledge, the students are asked to proceed what they can do remotely out of school while keeping close communication. Furthermore, they will also have experimental practice in the second semester, which started to take in UC-win/Road and debris-flow simulation for the first time from last 2019. He says that he would like to realize learning effect again like the previous year by working out better class organization, for example, dispersing students.
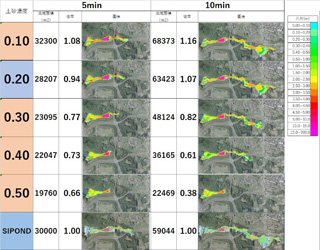 |
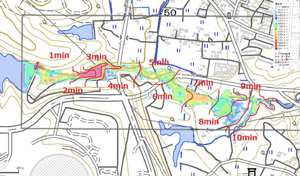
| Analysis conditions and results |
 |
 |
Hazard map based on the analysis result of
SIPOND (trial version). (This figure shows
simulation made by Prof. Mae by originally setting
numerical values) |
Hazard map based on the analysis result of
debris-flow simulation |
|
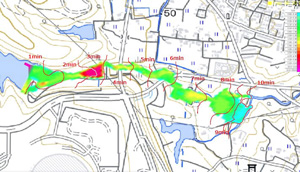
|  |
| Case examples of visualization with UC-win/Road |
Future Direction of Research and Application of ICT
"Not only Oita but also in other prefectures, there are many deteriorating reservoirs."
That is, in addition to deterioration, the mud flowing from the upper reach pile up on the bottom, and there are more and more risks of breach and overflow year by year, according to him. Associate Professor Mae talks about his idea that leads to research on disaster prevention and mitigation of reservoirs or their maintenance, to which he and others are currently committed.
He says that the key to realizing them is to respond to new technologies and acquire them. In consideration of the present situations under the limited condition of new coronavirus, it is eventually important to face ICT voluntarily for making wide progress in the use of ICT.
"In particular, as ICT can be a weapon to use anywhere (for the students in the future), I think it will be good for them to cope with ICT passionately and greedily."
|