|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
As his own study subjects that he has been focusing on in recent years, Prof. Kurihara mentions the following:
In the Lab, there are one first year master's student and eight fourth-year undergraduates. The latter includes two female students. Innovation in Anticipation of Social Needs at the 90th Anniversary of the Founding Tokyo City University was founded in 1929 as Musashi Senior Engineering School with 3 engineering departments of electricity, civil engineering, and architecture. Since then, after repeated renaming and expanding, the school was renamed Musashi Institute of Technology in 1949 under the Educational Reform Law, having Faculty of Engineering composed of 3 engineering Departments of Machinery, Electricity, and Construction, to make a new start. The school then kept on increasing faculties and reorganizing, establishing Graduate School of Engineering (doctoral and master's courses) and increasing majors step by step. In 1997, the Faculty of Environmental and Information Studies was established, and in 2007, the Faculty of Knowledge Engineering was established. In 2009 at the 80th anniversary of the founding, the school was renamed Tokyo City University, which is the current name. At the same time, the Faculties of Urban Life Studies and Human Life Sciences were established. In addition, in 2013, the Faculty of Environmental and Information Studies was reorganized into the Faculties of Environmental Studies and Informatics. In 2019, the University reaches the 90th anniversary of the founding. At present, Tokyo City University is composed of 6 Faculties of Engineering, Knowledge Engineering, Environmental Studies, Informatics, Urban Life Studies, and Human Life Sciences; and Graduate Schools of Integrative Science and Engineering, Engineering (name is changed to "Graduate School of Integrative Science and Engineering" for the students who enroll in and after 2018 fiscal year), and Environmental and Information Studies. The number of students of both undergraduate and graduate students is about 7,500 in total, while the number of full-time faculties is 286 (both figures are as of May 2018). 3 campuses in Setagaya, Yokohama, and Todoroki are situated as the base for education and studies. The Faculty of Engineering consists of 8 Departments of Mechanical Engineering, Mechanical Systems Engineering, Medical Engineering, Chemistry and Energy Engineering, Nuclear Safety Engineering, Architecture, Urban and Civil Engineering, and Electrical and Electronic Engineering (scheduled to be renamed Electrical, Electronic Communication Engineering). It is located in Setagaya Campus. Department of Urban and Civil Engineering, which responds to a wide range of social demands about cities and targeting engineering for improving urban quality beyond the category of conventional civil engineering, holds more than 400 students. Not only "Disaster Mitigation Lab" including "Kurihara Lab" but also Laboratories of Planning Management, Water Park Environment, Geotechnical Environmental Engineering, and Structural Safety, each of which contains subdivided laboratories. Deliberate Mechanism of "Urban Design Drawing" and Flow of Class "I had been teaching in the university for 29 years, and this class is one of my masterpieces." In order for students to learn practical design, it is essential for them to do actual work at the same time. When doing so, it is also important that the contents of a student's work is entirely different from those of other students. However, if the degree of freedom is too high, the class may diffuse too much. Therefore, basically it is necessary to follow professional design procedure. In this sense, the method of "Urban design drawing" mentioned at the beginning is truly a solution that take account of, and satisfy all of these elements, says Professor Emeritus Yoshikawa. About 10 years ago, he and Associate Prof. Kurihara and others played a leading role in examining whether they could develop an educational method to allow students to learn seismic design calculation of RC bridge piers efficiently and in a short time using a software package on the market for such part that is hard to work on by manual calculation. In that process, they paid attention to "UC-win/Section" as a software package to use, partly because software packages of FORUM8 had been introduced for research before. Using this, a system was built up in such a way that design practice seminars, which also serve as an opportunity to learn how to use a tool for practical calculation, are given twice a week (200 min.) contained in classes for 14 weeks. TA for assisting the teaching faculty was also provided.
Currently, nearly 50 students of the Department of Urban and Civil Engineering, which is almost half of third-year students (nearly 90) are taking the design seminar for the second semester of the third-year of the Dept., "Urban design drawing/seismic design of RC piers", which almost follows this framework. In this seminar, students are given 3 assignments in stages for which they are required to submit a report (calculation sheet) for each one:
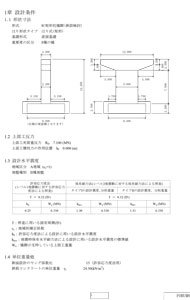
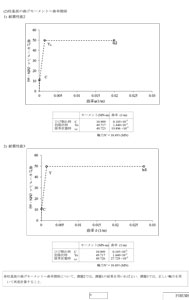
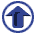
In specific, Assistant Prof. Kurihara prepares 60 to 70 different sets of design conditions in advance at each time. For Assignment 1, in order to confirm resistance to earthquakes of the pier base based on the set conditions, each of the students make a section analysis and calculate M-φ relationship and bending yield strength. At that time, each of the students is given different figures, size, design conditions etc. Since they have influence on the following assignments, it is so mechanized that one student has to cope with his or her own assignment and make calculation without relying on another student. For Assignment 2, a student makes seismic design calculation based on the section the student determined by him- or herself in Assignment 1, using the simple excel sheet created originally for the allowable stress method, and UC-win/Section for the horizontal capacity method. "To tell the truth, in Assignment 2, the initial settings are given so that the judgment of resistance to earthquakes will be 'OUT'". That is, each student should not only make judgment based on calculation by each one but also judge why the check result is "OUT". For example, through trial and error in the process, students may recognize something that is hard to learn only by the lecture, e.g. importance or effectiveness of main reinforcement or horizontal restraining reinforcement. Furthermore, in the following Assignment 3, students are required to change bar arrangement so that it meets the design criteria (obtains "OK"), make seismic design calculation again, and prepare the final report, according to Associate Prof. Kurihara. Expanding Availability of Software both in Terms of Education and Research "A good software program can be used also for engineering education," says Prof. Emeritus Yoshikawa. Prof. emeritus Yoshikawa has been experiencing the design seminar for 10 years. Through appropriate use of software on the market as well as actual design calculation sheet, the students learn the process of practical designing, and those who master the skill quickly support other students. He says that he has been actually feeling the effectiveness of these attempts by seeing such scenes. On the other hand, in "Urban Design Drawing" of the second semester this fiscal year, Mr. Keisuke Hashimoto, master's first year, the Division of Architecture and Civil Engineering, Graduate School of Integrative Science Engineering, and Mr. Takuya Yoshida, fourth-year undergraduate of the Department of Urban Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, both of whom belong to Kurihara Lab., take charge of TA (teaching assistant). They support Associate Prof. Kurihara, and instruct the students directly about how to use UC-win/Section or equations as needed. From this point of view, they mentioned their impression about easiness and visibility of making structural analysis with the software. Associate Prof. Kurihara says that so far high weight has been attached on studies regarding the area of material of concrete, and that in recent years, the range of studies are becoming larger to include the area of its structure. "The property of concrete changes a little from when it is in the condition of the material to when it is executed into RC structures. We would also like to incorporate examination of what this difference is like into our study (in the future). This requires verification using software programs like this. We plan to prepare different devices."
|
||||||||||||||
| (Written by Takashi Ikeno) (Up&Coming '19 New Year issue) |
||||||||||||||
|
||||