We will introduce three points which are improved in this new version.
The multi-thread process is improved to reduce the calculation time for
large models with plate elements. For example, the measured result of "61,000
nodes + 14,000 spring elements + 21,000 plate elements + 6 steps of analysis"
is displayed in Table 1.
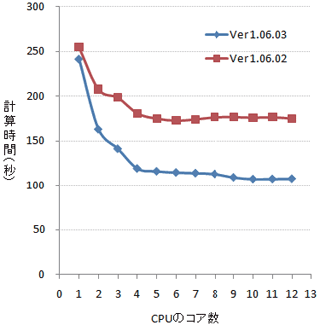
The calculation time is the processing time of solver. It does not include
pre/post processing time. The solver consists of two types of part: the
part that can do simultaneous parallel processing by dividing the processing
units, and the part that can only do uniprocessing. The vertical axis in
the graph indicates the processing time for both processes. According to
the figures, we can see that the calculation time is reduced in Ver.1.06.03.
When the number of cores increase from one to two, from two to three, and
from three to four, time is effectively reduced. But increasing further
from four will not make much of a difference in time. If you want to use
other software comfortably while calculating a large model, we can say
that using a high-performance computer with from eight to twelve cores
(logical core) is the most cost-effective way. The horizontal axis in the
graph indicates the uniprocessing time of solver. We will improve the processing
speed further by also looking into this part. "BMR(CD) damper"
was added to the non-linear property of spring elements. This is one type
of bridge beam's appendage, which is the compression damping system with
back up function, and sold by OILES Corporation. It provides the damping
effect of repetitive earthquake(Figure4). Moreover, a tool which allows
"loading, calculation, saving of the result" of the multiple
data files(*es) in order has been added. The es files in the folder can
be automatically processed by specifying the folder.
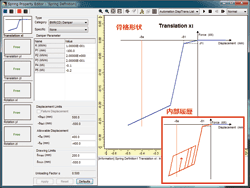 |
 Figure4: Spring property "BMR(CD) damper" model Figure4: Spring property "BMR(CD) damper" model |
 |
| Core |
Ver.1.06.02 |
Ver.1.06.03 |
| 1 |
255 |
242 |
| 2 |
208 |
163 |
| 3 |
198 |
141 |
| 4 |
181 |
119 |
| 5 |
175 |
116 |
| 6 |
173 |
115 |
| 7 |
174 |
114 |
| 8 |
177 |
113 |
| 9 |
177 |
109 |
| 10 |
176 |
107 |
| 11 |
177 |
107 |
| 12 |
175 |
108 |
|
 Table1:The number of cores of CPU and calculation time Table1:The number of cores of CPU and calculation time |
|