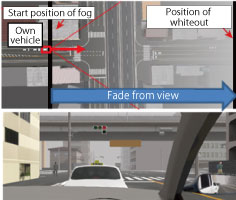
|
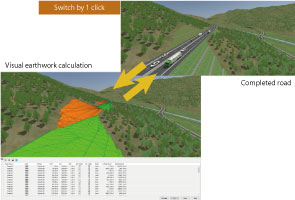
The earthwork volume calculation function has been added to the UC-win/Road Ver.13. This function allows users to calculate approximate volume of the earthwork by using the 3D shape of roads and terrains created in the software (Fig.1).
The use of 3D data in the civil engineering industry is becoming far more popular. This new calculation function uses the 3D shape of the earthworks for calculation instead of the common average section method.
After the intersection of road and terrain is calculated, roads are divided into two areas. One is the field where the road surface is higher than the terrain (banking), and another is the area where it is lower than the terrain (cutting). The volume between both surfaces is calculated by using the divided 3D surface shape data.
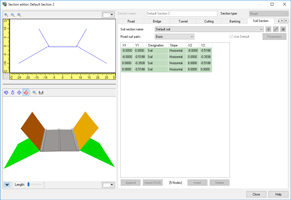
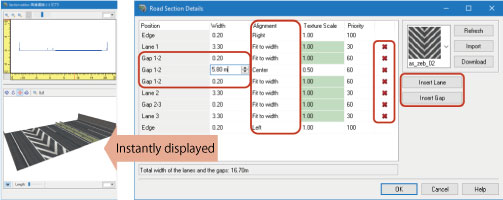
For calculating road surfaces, users now can select cross sections for civil engineering instead of the existing road cross section setting. The construction foundation and the embankment and cutting can be defined as with the current road cross section definition. Since default civil engineering cross section is automatically generated from existing road section, the volume of earthwork can be calculated after the normal data creation without any additional inputs (Fig.2).
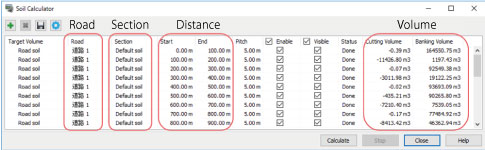
The amount of soil can be calculated by entering the road, earthwork cross section, distance from beginning to end, and pitch of the road surface. Users can define these items one by one, but also can use a batch creation function when calculating earthworking volume by a constant range or each cross section. Calculation by section enables the calculation of the cost including the amount of soil volume in each block. It can also be used for comparative review of different cross sections by using multiple earthwork cross sections.
|